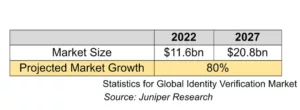
Identity verification is a big deal. Global spending on verification in 2022 hit over $11bn and is projected to leap to nearly twice that figure ($20.8bn) within a short five-year period.[1] The soaring spend is not much of a surprise, given the explosion of digital services across all spheres of life, governance and business which require digital onboarding, coupled with the alarming ubiquity of digital frauds, all leading to the need for well-developed comprehensive identity verification systems. Giant corporations like Microsoft and LexisNexis Risk Solutions are at the forefront of investments and infrastructural development within the space as business and regulatory services such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) continue to lean heavily on digital identity verification.
The prevailing reality of the twenty-first century is that businesses and other service providers are impelled to keep turning to digital channels in rendering their services as citizens’ lifestyles and livelihood are increasingly weaved around digital options and alternatives. Consequently, continued success and security in a hyper-digitalised world requires an understanding of the implications of digital dependency vis-à-vis identity verification, a rich knowledge of related trends, and a continuous rapid development and adoption of innovative approaches to such key services as KYC and client risk tiering.
What Is KYC and Why Is It Important?
KYC (Know Your Customer) is a standard practice of companies in which they verify the identity of their customers while adhering to established laws and regulations
governing data concerns and financial security such as Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws, Combating the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) laws, and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). While KYC is relevant in various sectors of the economy, it takes principal place in the finance industry and occupies a cardinal position with fintech and non-fintech service providers, including banks, insurance companies, investment firms, real estate outfits, cooperatives, savings, and lending firms. Issues bordering on customer identity authentication, consumer data protection, credit risk assessment, cyber security and fraud are directly impacted by KYC, hence, it is of key interest to regulatory establishments in the finance space and in many cases a mandatory element for customers to access financial services. In Nigeria, the Central Bank of Nigeria regulates the overall KYC process and in 2013, it furnished a three-tiered KYC requirement process to which financial service providers are to comply.
Why Are Digital Methods Required for KYC?
Across the globe and in all of industry, accelerated digital revolution and the continued rapid emergence of new digital technologies have necessitated quantum shifts from reliance on physical processes to digitally-enabled virtual processes. Moreso, the Covid-19 global pandemic and its attendant restrictions on physical engagements further reinforced reliance on the use of digital technology across board. Initially, KYC processes were mostly in-person, requiring physical data-capturing and physical submission of statutory documents, with little use of advanced technology. But the combined forces of digital revolution and post-pandemic realities have intensified the need for and use of digital methods in KYC. Digital KYC has fast evolved from a nice-to-have to a need-to-have.
With Digital KYC, concerned parties benefit in numerous ways. The necessary identity verification process is now easier and faster for customers as they can go through the entire process remotely. Onboarding is also more customer-centric and customer experience stands a better chance at being optimised with the availability of technology. Additionally, turnaround time for accessing desired financial services is shortened for customers. For service providers, comprehensive data gathering and due diligence are made possible via Digital KYC while required ongoing data and process monitoring are made easier.
Furthermore, Digital KYC better equips service providers to mitigate incidences of fraud and comply better with anti-money laundering laws.
What Issues are Emerging and What Are the Possibilities for Advanced Digital Methods in KYC?
With the several benefits of digital methods in KYC, certain issues keep emerging. Increasingly, more sophisticated approaches are being engaged by hoaxers to execute fraud and identity theft. As at the end of 2021, the global cost of cyber-crime hit $6 trillion. The Nigerian Communications Commission puts the country’s loss to cyber-related fraud at $500m in 2022 alone, with stronger techniques being deployed by scams. These issues call for more innovative and collaborative approaches in deploying digital methods for identity verification.
One of such innovative approaches is being demonstrated by Swiftend
Swiftend – Identity Verification Service, a digital identity verification platform that incorporates authority databases intoidentity verification process thereby creating a fool-proof and robust mechanism for identity, address and company verification. With advanced and more secure API technology, Swiftend accesses authority databases for details captured in government-issued IDs such as National ID, International Passport, Driver’s Licence, Tax Identification Number, Voter Identification Number, and even Company Registration Number. Swiftend also accesses databases of financial standing such as Bank Verification Number, Account Numbers, Credit Reports, Transaction Profile, Utility Data, and data from Mobile Network Operators. Swiftend’s strategy and approach to KYC typifies a working collaborative model and proves that the possibilities within the identity verification space are better harnessed not only through individual ingenuity but through a broad-based synergistic orientation.
What Does the Future Hold for KYC?
As broad-scale digitalisation continues, identity verification will continue to hold a strong position in helping to ensure process efficiency and in curbing the inevitable exposure to heightened cyber risks. Regulation will continue to play a significant role in KYC, hence, deliberate networks and collaboration need to be built between regulators and innovators to birth a more united front in advancing Digital KYC and providing more impenetrable digital systems and mechanisms for identity verification and against fraud. As with several other areas, the digitalisation of KYC will continue its forward march and better options will continue to be introduced into the market as advanced technologies like blockchain and machine learning are increasingly leveraged by Digital KYC service providers. Hence, financial service providers, especially in Africa, will need to be more open, proactive and nimbler in sourcing and adopting digitally advanced mechanisms as they emerge if they must stay competitive in the market. In the end, the future of KYC is digital, and only the digitally impassioned will thrive in it.
* Sadiq Arogundade is the Founder/CEO of D’Accubin Technology Limited Swiftend.com, the creators of WhoisID.africa, a digital address verification platform that utilizes algorithms that leverage geocodes/IP addresses as well as GPS position triangulations to digitally validate addresses. WhoisID.africa is aiming to simplify the KYC process and disrupt the identity verification industry in Africa.
Sadiq Arogundade, a skilled expert in compliance, corporate governance, and financial risk mitigation with rich experience spanning over a decade in building technology solutions, shares his thoughts on the trends, developments and future of identity verification in Africa and suggests novel approaches to building new solutions and realising new possibilities.
[1] Juniper Research, 2022