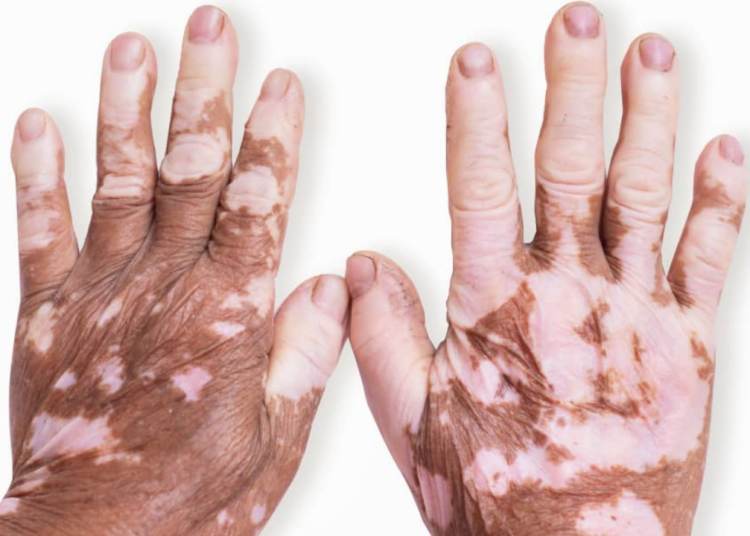
Vitiligo is a skin condition that causes one’s skin to lose its colour or pigment. It causes patches of skin to lose their colour, making the skin appear lighter than the natural skin tone or turn white.
This skin disorder can occur in people of any age, sex, and ethnicity. The condition can cause skin colour loss in various areas of the body.
Once vitiligo develops, it is usually a lifelong condition. However, there might be a 10 to 20 per cent chance that the skin’s natural colour will be restored, especially if the person is young.
Causes or Risk Factors:
The patches appear when melanocytes (the cells responsible for producing melanin) within the skin are destroyed.
Researchers now understand that vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder in which the body destroys parts of itself. It happens when a part of the immune system starts to attack and kill the pigment cells in the skin, resulting in the formation of white patches.
So why might the body’s immune cells attack healthy skin cells in the first place? That question is still not entirely settled among researchers, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. But it seems likely that genetics and environmental triggers both play a role.
Symptoms:
The symptom of vitiligo is the appearance of flat lighter-coloured spots or patches on the skin. This may start as a simple spot, a little paler than the rest of the skin, but as time passes, it becomes paler until it turns white.
Some people may have only a handful of white dots that develop no further, while others develop larger white patches that join together and affect more significant areas of their skin.
These spots can show up anywhere on the body, though they may first appear in areas that receive a lot of sun exposure, such as on the face, arms, feet, and hands.
Some people may also experience hearing loss, loss of eye pigmentation, and other autoimmune diseases, such as thyroid disease
Treatment:
Vitiligo is a health issue that needs medical attention. Several remedies can help decrease the visibility of the condition.
One of these remedies is the use of sunscreen. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends using sunscreen to protect the skin.
This is because the lighter patches of skin are especially sensitive to sunlight, and they can burn quickly.
A dermatologist can advise on a suitable type of sunscreen to combat vitiligo, among others.